Manhattan Physical Therapy
Physical Therapy & Acupuncture Located In NYC
Manhattan Physical Therapy
PHYSICAL THERAPY & ACUPUNCTURE LOCATED IN NYC
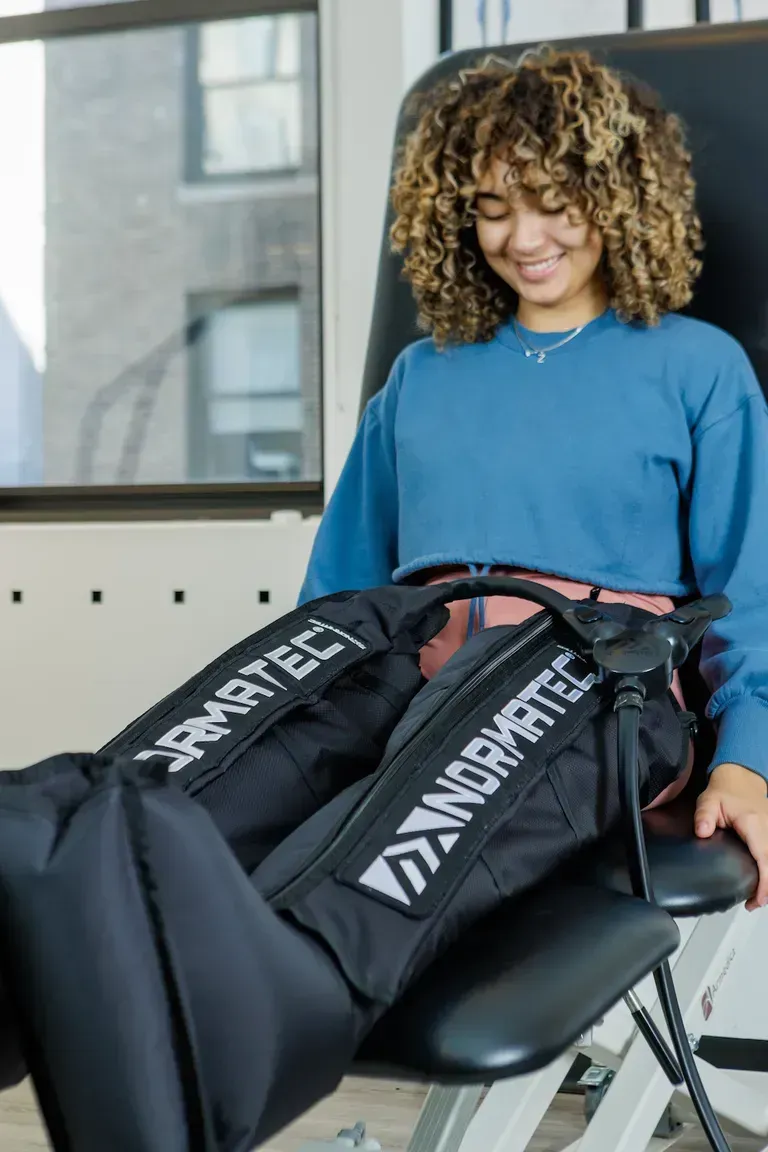

About Manhattan Physical Therapy
Manhattan Physical Therapy is a leading pain relief and injury ...
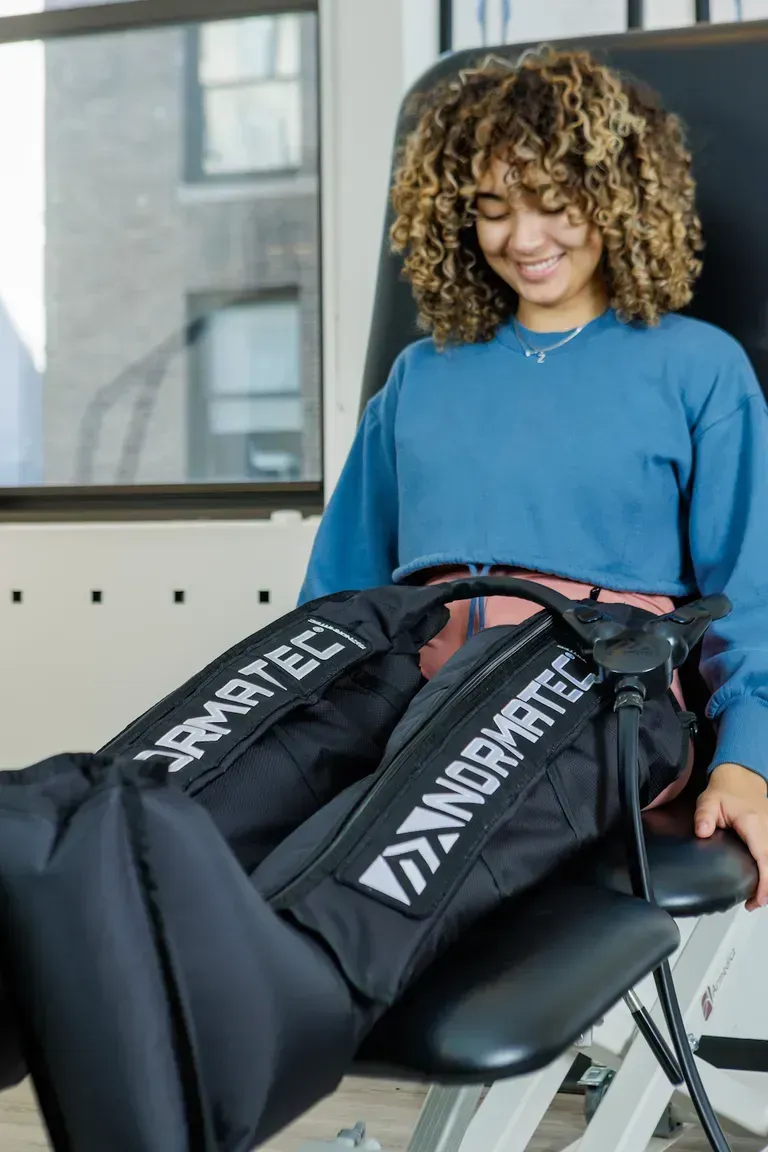

About Manhattan Physical Therapy
Manhattan Physical Therapy is a leading pain relief and injury ...
Services
Suspension Therapy
Bell's Palsy
Acupuncture
Sports Performance
3D Movement Scan
Diagnostics Ultrasound
Pelvic Floor
Pain Management
Services
Suspension Therapy
Bell's Palsy
Acupuncture
Sports Performance
3D Movement Scan
Diagnostics Ultrasound
Pelvic Floor
Pain Management
Meet The Doctors

Tiffany Zarcone, PT, DPT

John Miller

Bianca Guidotti, AT
Meet The Doctors

Tiffany Zarcone, PT, DPT

John Miller

Bianca Guidotti, AT
Our Mission
Manhattan Physical Therapy and Pain Center is a leader in pain relief and injury recovery located in Midtown New York City. Our mission is to help New Yorkers recover faster, move better, and avoid long-term pain by combining advanced technology, one-on-one care, and over 20 years of expertise.
Manhattan Physical Therapy and Pain Center has an excellent track record of success treating conditions such as back pain, ACL injuries, Bell’s Palsy, pelvic floor dysfunction, and post-surgical recovery.
Our Mission
Manhattan Physical Therapy and Pain Center is a leader in pain relief and injury recovery located in Midtown New York City. Our mission is to help New Yorkers recover faster, move better, and avoid long-term pain by combining advanced technology, one-on-one care, and over 20 years of expertise.
Manhattan Physical Therapy and Pain Center has an excellent track record of success treating conditions such as back pain, ACL injuries, Bell’s Palsy, pelvic floor dysfunction, and post-surgical recovery.
Insurances
We accept most major insurance plans, including Aetna, BlueCross BlueShield, Cigna, UnitedHealthcare, and Medicare. Please call our office to confirm your specific coverage.








Check Us Out On Social Media!
Insurances
We accept most major insurance plans, including Aetna, BlueCross BlueShield, Cigna, UnitedHealthcare, and Medicare. Please call our office to confirm your specific coverage.








Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Where is Manhattan Physical Therapy located?
A: We’re in Midtown Manhattan at 385 5th Ave, Suite 503, New York, NY 10016, near Penn Station and Bryant Park.
Q: Do you accept insurance?
A: Yes, we accept most major plans including Aetna, BlueCross BlueShield, Cigna, UnitedHealthcare, and Medicare. Call our office to confirm your coverage.
Q: What conditions do you treat?
A: We specialize in ACL rehab, Bell’s Palsy therapy, pelvic floor care, Redcord suspension training, chronic pain, and post-surgical recovery.
Q: What makes your clinic different?
A: We combine advanced diagnostics (ultrasound and 3D movement scans), Redcord suspension therapy, and one-on-one care to help New Yorkers recover faster and avoid long-term pain.
Q: How do I choose the right physical therapy in NYC?
A: Manhattan Physical Therapy offers specialized care in ACL rehab, Bell’s palsy treatment, pelvic floor therapy, and Redcord suspension to help New Yorkers recover faster.
Manhattan Physical Therapy
✆ Phone (appointments):
(212) 213-3480
Address: 385 5th Ave, Suite 503, New York, NY 10016